- Walsh, P. S., Metzger, D. A., and Higuchi, R. (1991) Chelex® 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques4, 506–513.Google Scholar
- Walsh, P. S., Varlaro, J., and Reynolds, R. (1992) A rapid chemiluminescent method for quantitation of human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res.20, 5061–5065.PubMedCrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Waye, J. S. and Willard, H. F. (1986) Structure, organisation and sequence of alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 17: evidence for evolution by unequal crossing-over and an ancestral pentamer repeat shared with the human X chromosome. Molec. Cell. Biol.6, 3156–3165.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whitehead, T. P., Thorpe, G. H. G., Carter, T. J. N., Groucutt, C., and Kricka, L. J. (1983) Enhanced luminescence procedure for sensitive determination of per-oxidase-labelled conjugates in immunoassay. Nature305, 158,159.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Velleman, S. G. (1995) Quantifying immunoblots with a digital scanner. Biotechniques18, 1056–1058.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Dot and slot blotting are simple techniques for immobilizing bulk unfractionated DNA on a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane. Hybridization analysis can then be carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations. Dot and slot blots differ only in the geometry of the blot, a series of spots giving a hybridization pattern that is amenable to.

Dot and slot blot hybridization
Abstract: This protocol describes how to prepare a DNA dot blot with a dot blot apparatus and a vacuum manifold. Author: Simon Dawson. Kube, Arun Srivastava; Quantitative DNA slot blot ysis. Dot and Slot Blotting of DNA.See the sample label below for the slot blot assay protocol location of this ati radeon 5770 single slot information.Our results demonstrate the importance of PtCAF-1 for the epigenetic trans-nuclear cross-talk mechanism.
Dna Slot Blot Protocol Test
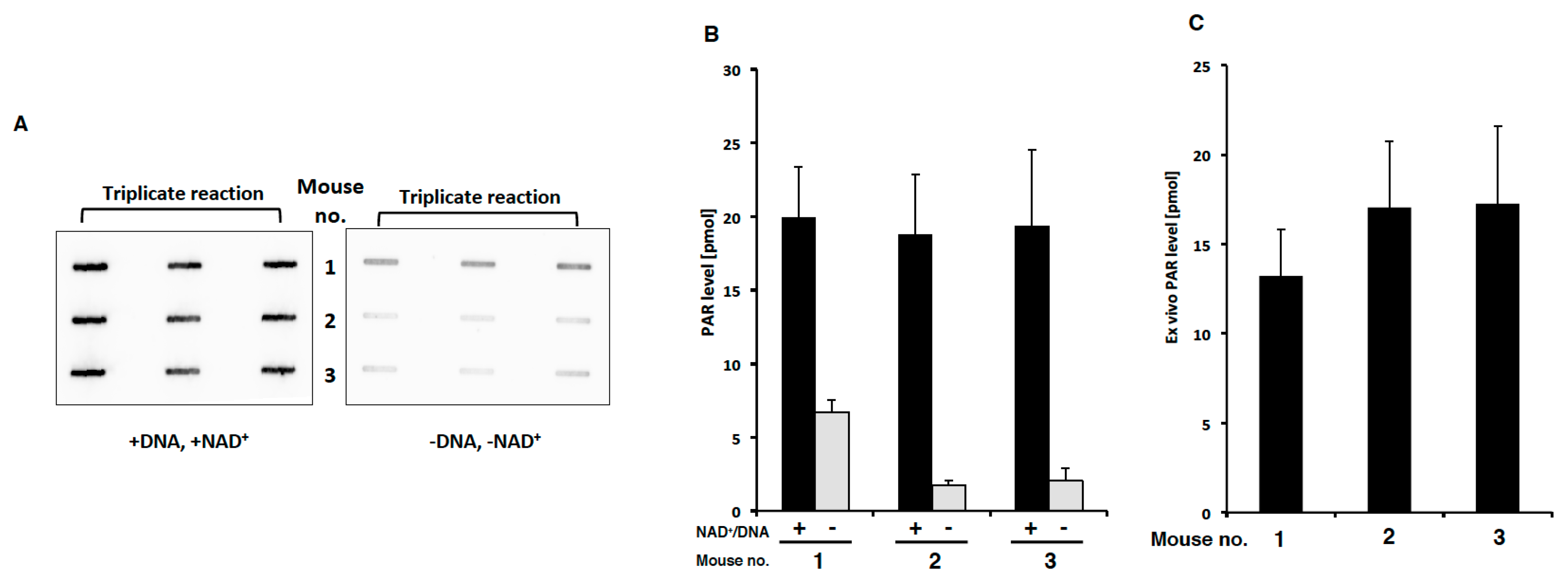
Often it is informative to quantify the abundance of a certain RNA or DNA in the extracted nucleic acid mixture by dot blot or slot blot hybridization without prior digestion and electrophoresis. In the procedure, the nucleic acid mixture is blotted to a membrane where the hybridization is carried out. The difference between dot and slot blot procedures is in the way that the nucleic acid mixture is blotted onto the membrane. In dot blotting the nucleic acids are blotted as circular blots, whereas in slot blotting they are blotted into rectangular slots (Figure 1). The latter method allows a more precise observation of different hybridization signal intensities. Quantification of a certain RNA/DNA compared with total RNA/DNA can be obtained by hybridization with universal and specific oligonucleotide probes. The relative abundance is calculated by dividing the amount of specific probe bound to a given sample by the amount of hybridized universal probe measured e.g. as fluorescence intensity (fluorescent probes) or counts per minute (radioactively labelled probes).

Dna Slot Blot Protocol Igg
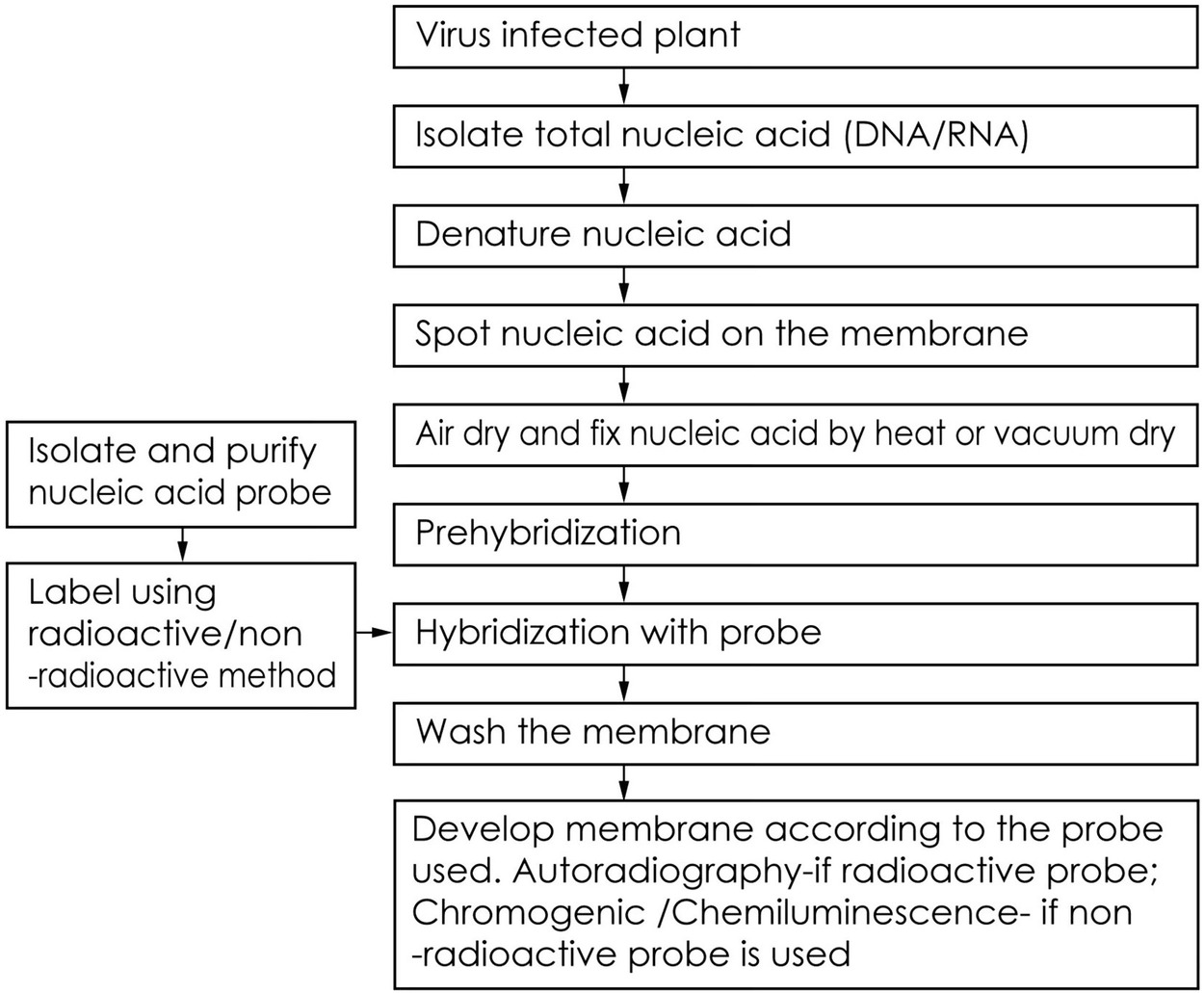
Figure 1. Dots and slots in dot and slot blot hybridization, respectively.
Dna Slot Blot Protocol Definition
One should be aware that the data of relative DNA or RNA abundance can not be directly translated into cell numbers. Cells may have different copy numbers of various genes. Moreover, cells of different species have different ribosome contents ranging roughly between 103 and 105 ribosomes per cell. Even for one strain, cellular rRNA contents can vary significantly (at least over one order of magnitude), since they are directly correlated with the growth rate. The relative rRNA abundance should, however, represent a reasonable measurement of the relative physiological activity of the respective population, since it is the product of the number of detected cells and the average rRNA content. This information on the general activity of a given population should not automatically be regarded as an indication of a specific kind of activity. Often, one population has the potential to catalyze different transformations - one genotype is linked to several phenotypes.